Abstract
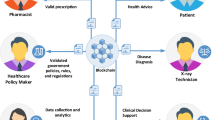
To address the private data management problems and realize privacy-preserving data sharing, a blockchain-based transaction system named Ecare featuring information transparency, fairness and scalability is proposed. The proposed system formulates multiple private data access control strategies, and realizes data trading and sharing through on-chain transactions, which makes transaction records transparent and immutable. In our system, the private data are encrypted, and the role-based account model ensures that access to the data requires owner’s authorization. Moreover, a new consensus protocol named Proof of Transactions (PoT) proposed by ourselves has been used to improve consensus efficiency. The value of Ecare is not only that it aggregates telemedicine, data transactions, and other features, but also that it translates these actions into transaction events stored in the blockchain, making them transparent and immutable to all participants. The proposed system can be extended to more general big data privacy protection and data transaction scenarios.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Casino, F., Dasaklis, T. K., & Patsakis, C. (2019). A systematic literature review of blockchain-based applications: Current status, classification and open issues. Telematics and Informatics, 36, 55–81.
Esposito, C., De Santis, A., Tortora, G., Chang, H., & Choo, K.-K.R. (2018). Blockchain: A panacea for healthcare cloud-based data security and privacy? IEEE Cloud Computing, 5(1), 31–37.
Wu, M., Wang, K., Cai, X., Guo, S., Guo, M., & Rong, C. (2019). A comprehensive survey of blockchain: From theory to IoT applications and beyond. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6(5), 8114–8154.
Dai, H. N., Zheng, Z., & Zhang, Y. (2019). Blockchain for internet of things: A survey. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6(5), 8076–8094.
Dinh, T. T. A., Liu, R., Zhang, M., Chen, G., Ooi, B. C., & Wang, J. (2018). Untangling blockchain: A data processing view of blockchain systems. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 30(7), 1366–1385.
Azaria, A., Ekblaw, A., Vieira, T., & Lippman, A. (2016). Medrec: Using blockchain for medical data access and permission management. The 2nd International Conference on Open and Big Data (pp. 25–30). Vienna: Austria.
Dagher, G. G., Mohler, J., Milojkovic, M., & Marella, P. B. (2018). Ancile: Privacy-preserving framework for access control and interoperability of electronic health records using blockchain technology. Sustainable Cities and Society, 39, 283–297.
Li, H., Zhu, L., Shen, M., Gao, F., Tao, X., & Liu, S. (2018). Blockchain-based data preservation system for medical data. Journal of Medical Systems, 42(8), 141.
Daraghmi, E., Daraghmi, Y., & Yuan, S. (2019). Medchain: A design of blockchain-based system for medical records access and permissions management. IEEE Access, 7, 164595–164613.
Nguyen, D. C., Pathirana, P. N., Ding, M., & Seneviratne, A. (2019). Blockchain for secure EHRS sharing of mobile cloud based e-health systems. IEEE Access, 7, 66792–66806.
Li, X., Huang, X., Li, C., Yu, R., & Shu, L. (2019). Edgecare: Leveraging edge computing for collaborative data management in mobile healthcare systems. IEEE Access, 7, 22011–22025.
Liu, X., Ma, W., & Cao, H. (2019). MBPA: A medibchain-based privacy-preserving mutual authentication in TMIS for mobile medical cloud architecture. IEEE Access, 7, 149282–149298.
Liu, Y., Wang, K., Lin, Y., & Xu, W. (2019). LightChain: A lightweight blockchain system for industrial internet of things. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 15(6), 3571–3581.
Truong, N. B., Sun, K., Lee, G. M., & Guo, Y. (2019). GDPR-compliant personal data management: A blockchain-based solution. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 15, 1746–1761.
Dai, W., Dai, C., Choo, K. K. R., Cui, C., Zou, D., & Jin, J. (2019). SDTE: A secure blockchain-based data trading ecosystem. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 15, 725–737.
Jiang, S., Cao, J., & Yang, Y. (2021). Fairness-based packing of industrial IoT data in permissioned blockchains. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 17, 7639–7649.
Ferrag, M. A., & Shu, L. (2021). The performance evaluation of blockchain-based security and privacy systems for the internet of things: a tutorial. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 8(24), 17236–17260.
Ferrag, M. A., & Maglaras, L. (2020). DeepCoin: A novel deep learning and blockchain-based energy exchange framework for smart grids. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 67(4), 1285–1297.
Wang, Y., Zhang, N., Chen, J., Sun, X., Ye, Z., & Zhou, Z. (2021). SPDS: A secure and auditable private data sharing scheme for smart grid based on blockchain. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 17, 7688–7699.
Xu, L., Bao, T., & Zhu, L. (2021). Blockchain empowered differentially private and auditable data publishing in industrial IoT. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 17, 7659–7668.
Yu, K., Tan, L., Aloqaily, M., Yang, H., & Jararweh, Y. (2021). Blockchain-enhanced data sharing with traceable and direct revocation in IIoT. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 17, 7669–7678.
Castro, M., & Liskov, B. (2002). Practical byzantine fault tolerance and proactive recovery. ACM Transactions on Computer Systems, 20(4), 398–461.
Xu, J., Xue, K., Li, S., Tian, H., Hong, J., Hong, P., & Yu, N. (2019). Healthchain: A blockchain-based privacy preserving scheme for large-scale health data. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6(5), 8770–8781.
Ai, Z., & Cui, W. (2022). A proof-of-transactions blockchain consensus protocol for large-scale IoT. IEEE Internet of Things Journal. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2021.3108627
Ecare. (2021). https://github.com/azd1997/Ecare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Key R &D Program of China (No. 2018YFB1700100) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61873317)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, W., Pan, Y. & Ai, Z. A blockchain-based transaction system for private data sharing and trading. Control Theory Technol. 20, 291–302 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11768-022-00098-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11768-022-00098-8